English

Capacidades
Creación rápida de prototipos y fabricación bajo demanda.

Industrias
Únase a miles de líderes de la industria que impulsan la innovación de productos con Chiggo.
Dispositivos médicos
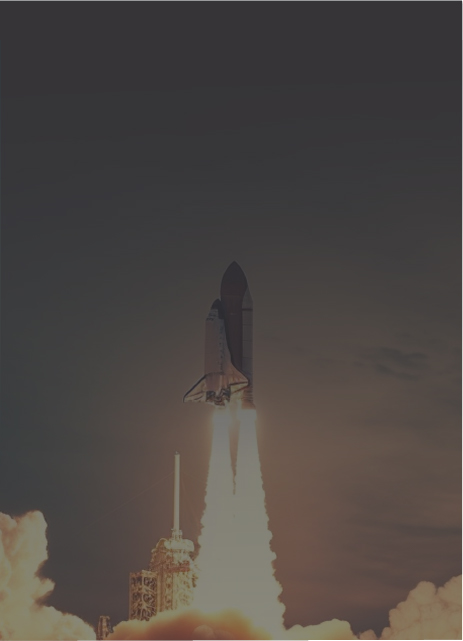
Aeroespacial
Productos de consumo
Equipos industriales
Ofrecer innovaciones de forma rápida y segura a la atención sanitaria
Impulsar proyectos desde el plano hasta el despegue con eficiencia
Dando forma a productos que definen la vida moderna, desde la idea hasta el uso
Impulsando el progreso con maquinaria avanzada para una productividad superior

Soluciones
Una solución integral desde las materias primas hasta la producción y la mejora del producto.

Sobre nosotros
Descubra quiénes somos y cómo garantizamos la calidad y la entrega oportuna.
Acerca de Chiggo
Acerca de la entrega
Seguro de calidad
Nuestra fábrica
Nuestra visión, misión, historial de desarrollo y equipo dedicado.
Tiempos de respuesta rápidos y eficientes, optimizando cada paso desde la realización del pedido hasta la entrega.
Entregamos prototipos rápidos de calidad y piezas de producción bajo demanda que cumplen y superan las expectativas.
Descubra la precisión y la innovación detrás de Chiggo con un recorrido por nuestra fábrica, disponible en línea o in situ.

Recurso
Todo lo que necesitas saber sobre la fabricación digital.
-
Blog
-
Video
Su fábrica de fuentes confiablesDesde 2011











-NC加工-448X301.jpg?width=448&height=301)














































