English

行业
加入成千上万的行业领导者的行列,与 Chiggo 一起推动产品创新。

解决方案
从原材料到生产和产品增强的一站式解决方案。

资源
您需要了解的有关数字化制造的一切。
3D打印和CNC加工是最受欢迎的两个制造过程今天。两种方法都依赖数字控制系统来快速生产原型,并适合创建准确的定制最终用途零件。
但是,它们几乎在各个方面都有不同 - 在生产坚固的零件方面,它们甚至是直接的竞争对手。最大的区别是一种方法逐层构建零件,而另一个方法是通过删除材料来构建零件的。如果您发现自己在CNC加工和产品的3D打印之间进行选择,请继续阅读以了解更多信息。
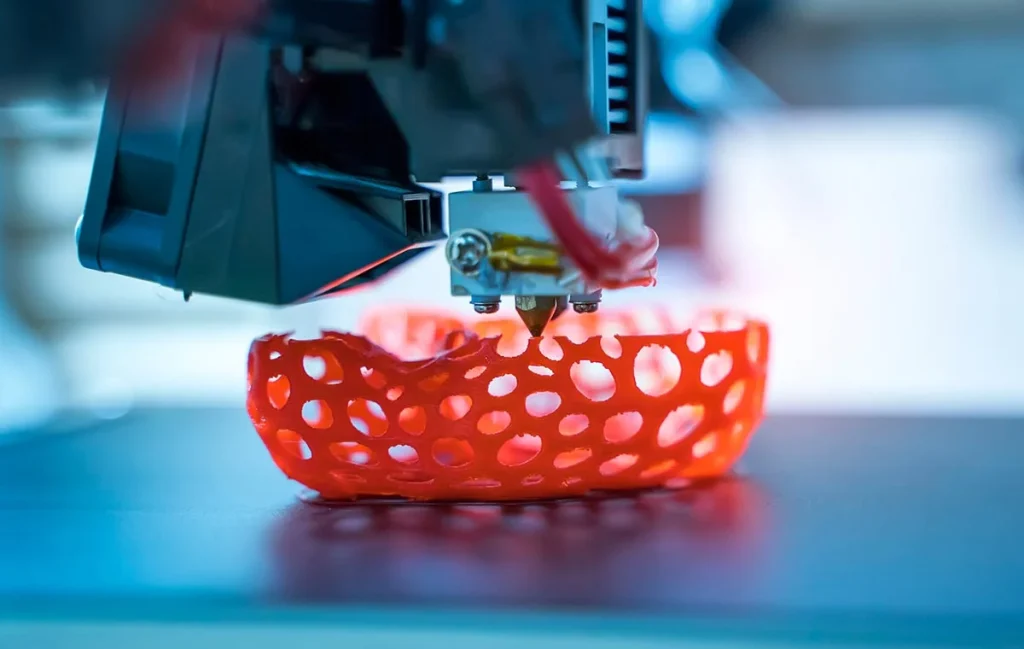
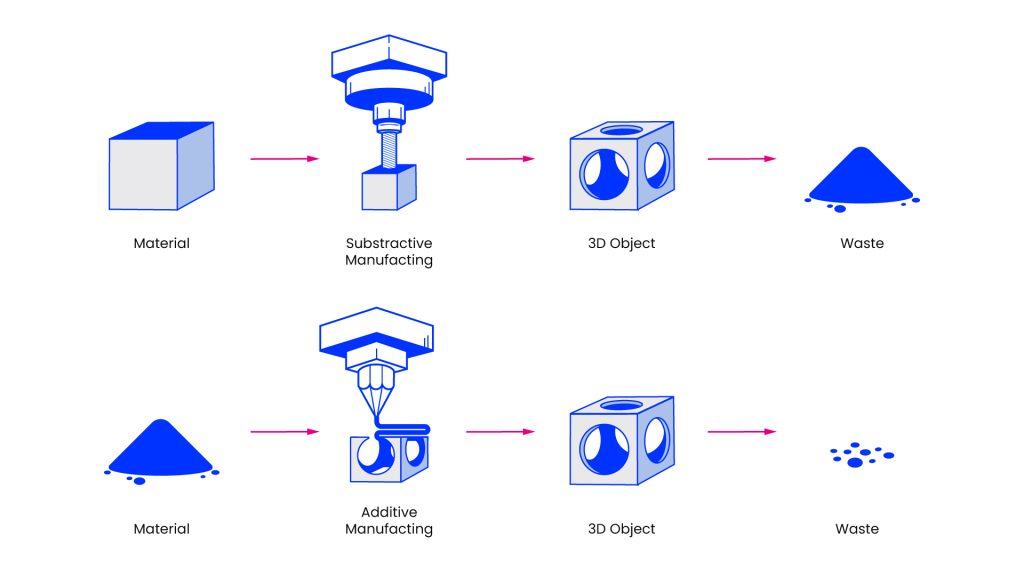

3D打印,也称为增材制造,是一个过程,它通过逐层添加材料来从数字模型中创建三维对象。该过程始于数字模型,该模型可以使用从3D扫描仪获得的CAD(计算机辅助设计)软件创建,也可以从在线存储库中下载。接下来,将模型导入切片软件,该软件将其分为许多二维横截面层,这些层用作打印机的蓝图。然后,切片软件将这些层转换为一系列指令(通常是G代码),即3D打印机可以理解。此外,如果该模型包含悬垂零件,则该软件可能会生成支持结构以确保正确打印。最后,打印机遵循这些说明,通过一层沉积材料,并将每个新层粘合到其下面的一个,并逐渐构建完整的对象。
1980年代后期,查克·赫尔(Chuck Hull)发明了立体光刻(SLA),这是第一个3D打印技术。随着新材料和技术进步的持续研究,出现了更多的3D打印技术。今天的常见类型包括:
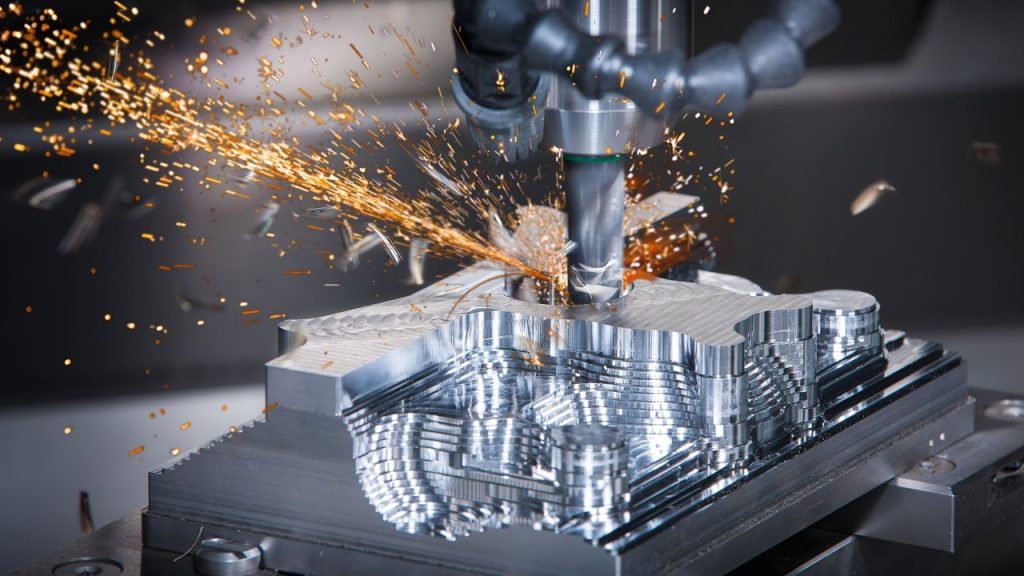

尽管3D打印是一个尖端的添加剂制造过程,但CNC加工(计算机数值控制加工)代表了一种更传统的减法制造技术。 CNC加工在1950年代从1950年代出现,随着数字自动化的发展,CNC加工已经发展起来,从而使整个行业都可以高精度制造。
要获取CNC部分,您首先使用CAD软件创建数字模型。然后,通过CAM编程将该模型转换为机器可读的G代码,该编程指定了精确的运动,速度和操作。之后,工件牢固地安装在CNC机器上,并选择和安装适当的切割工具。 CNC机器遵循G代码:从粗加工开始,以去除多余的材料,然后继续进行精细加工以实现最终的尺寸和表面光洁度。
在制造业中广泛使用的CNC加工有几种常见类型:
两种技术都具有独特的优势 - CNC加工具有高精度和材料的多功能性,而3D打印是创建复杂的几何形状和快速原型制作的优选。它们之间的选择取决于各种因素,包括材料需求,设计复杂性,生产速度和预算考虑。
下面的快速检查表提供了简短的比较,可帮助您确定哪种过程最适合您的需求,或者两者的组合是否可能产生最佳结果。
| 因素 | 3D打印 | CNC加工 |
| 材料选择 | ▪ Limited but expending options ▪ Flexible materials and superalloy | ▪ Wide range , including metals, plastics, wood, and composites |
| 设计复杂性 | ▪ Can achieve highly complex geometries, including lattice structures and organic shapes | ▪ Can produce parts with relatively complex features, such as threaded holes, sharp edges, and curves ▪ Limited by tool accessibility, tool path and type, axis-defined minimum radii, and the need for repositioning during the process |
| 精确 | ▪ Moderate precision, typically ±0.1 mm, though high-end printers can achieve tighter tolerances | ▪ High precision, often ±0.005 mm or better, depending on material and machine ▪ Excellent repeatability |
| 表面饰面 | ▪ Requires post-processing (e.g. sanding, painting) for a smooth finish ▪ Some 3D printing processes produce surfaces that are grained, rough, and stepped, or features that may appear blurred | ▪ Smooth finish with little to no post-processing (typical 125 Ra finish as machined) |
| 大零件尺寸 | ▪ Up to 914 x 610 x 914 mm (e.g. FDM) ▪ Ideal for smaller prototypes or assemblies | ▪ Up to 2000 x 800 x1000 mm ▪ Suitable for industrial housings and large-scale prototypes |
| 力量 | ▪ In FDM, layer adhesion and print orientation reduce the strength of parts ▪ Metal 3D printed parts in SLM and DMLS offer strength comparable to or even better than traditionally machined parts, especially when heat-treated or made with specific alloys | ▪ The internal structure of parts is continuous, and their strength usually remains at 100% of the native material ▪ Some high-strength alloys may be impossible or difficult to process with extreme precision |
| 设置 | ▪ Minimal setup, require only a digital file and slicer software | ▪ Need workpiece fixation, tool selection, and machine calibration ▪ G-code programming,toolpath generation, and potential part repositioning |
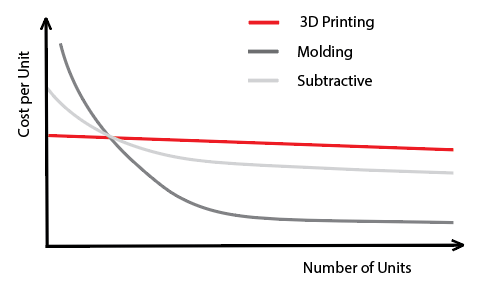
| 构建速度 | ▪ Low setup time, but build time can take hours ▪ Quicker for small batches and complex designs ▪ Ideal for design validation, rapid prototyping, and test fits | ▪ Can take ages to set up and program, but cutting can be very fast ▪ Fast for bulk production |
| 成本 | ▪ Cost-effective for small series or custom one-offs ▪ Slight variations in your product’s size can significantly increase your 3D printing manufacturing costs | ▪ More economical for high-volume production ▪ More material waste |
接下来,我们可以通过询问以下一系列问题来确定您是否应该选择CNC加工,3D打印或两者为您的项目。
3D打印和CNC对金属和塑料进行加工。 CNC加工具有更广泛的材料适应性。尽管塑料变得越来越受欢迎,但它主要用于从金属生产零件。您也可以使用CNC工艺来制造木材,复合材料,甚至泡沫和蜡的零件。
最常见的CNC材料:
3D打印主要与热塑性,树脂和一些金属粉末一起使用。但是,3D打印的金属零件并不便宜,尽管情况正在发生变化。
常见的3D打印材料:
值得注意的是,非常柔软,柔性的材料(例如TPU和硅酮)在切割力下倾向于变形,从而使精确的加工变得困难。同样,某些超级合金由于高强度,工作硬化和耐热性而对机器的挑战。对于这些材料,3D打印可能是一个更好的选择。
尽管5轴或更高级的机器可以处理非常复杂的几何形状,但由于工具无法访问该部件的所有表面,因此仍然很难(甚至不可能)创建隐藏的功能和底切。切割工具本身的几何形状也限制了加工完美正方角的能力。此外,通常需要定制固定装置或夹具,这可能是一个重要的限制。
3D打印机消除了CNC加工中的这些几何挑战。它们可以相对轻松地产生高度复杂的几何形状。尽管SLM等过程可能需要支持结构,但额外的后处理并没有降低3D打印提供的巨大设计自由和复杂性。
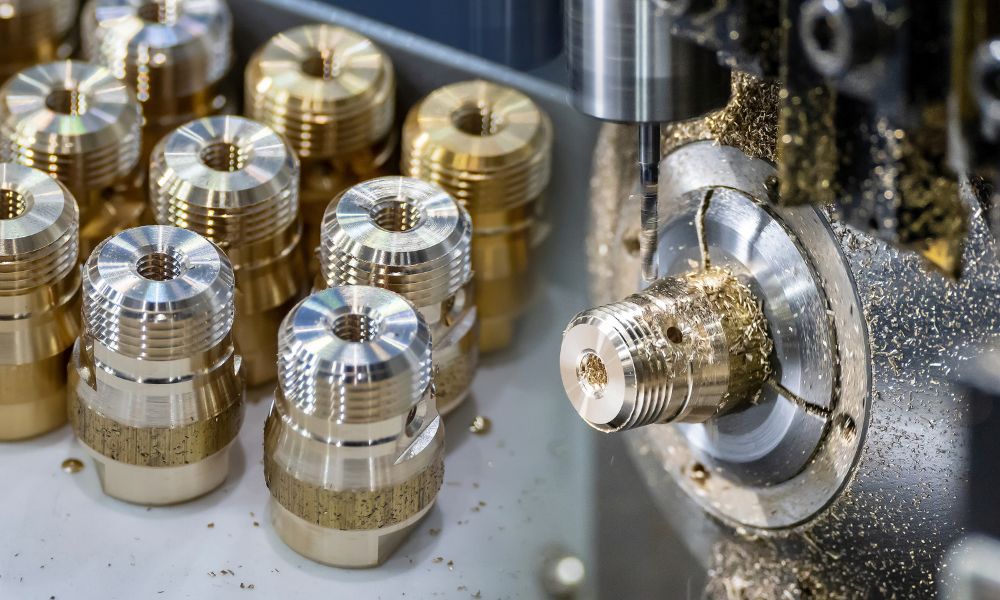

由于材料收缩和打印过程的分辨率限制,因此3D打印通常不如CNC加工精确。例如,在标准条件下,诸如SLA之类的精确3D打印技术通常达到±0.1mm的公差。相比之下,精确的CNC机器可以容纳高达±0.025mm(0.001英寸)甚至更好的公差。
当涉及重复性3D打印时,即使是SLA或DLP等高精度方法,仍然落后于CNC加工。 CNC机器由于其刚性机械设置,精确的控制系统以及减法过程的均匀性提供了较高的一致性。相反,3D打印更容易受到材料收缩,层粘附和环境因素引起的变异性。
像SLA这样的3D打印机可以生产具有细,光滑和纹理层的零件,但是使用正确的工具的CNC加工可以实现甚至更光滑的表面。
可以通过各种表面完成选项提高零件的功能和外观品质。例如,CNC加工的零件可以阳极氧化,粉末 - 粉末,粉状,珠子涂成珠和言行。同样,3D打印零件的表面整理选项包括 plating ,,珠子爆破,抛光,抛光,抛光和热处理以增强产品。
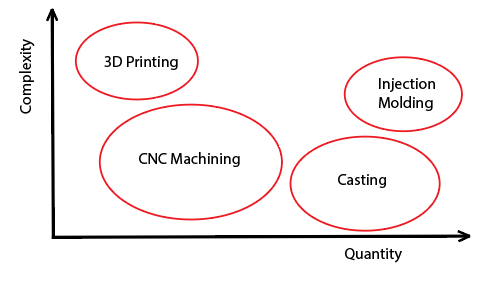
对于具有典型几何形状的部分(可以通过CNC相对容易实现的部分),选择取决于零件的材料和数量。
塑料零件:
对于金属零件,情况大不相同:
为您的自定义零件选择正确的制造技术似乎是一个无法克服的挑战,但这并不是一定。正如我们总是在Chiggo告诉客户,没有完美的,适合所有的制造方法。最佳选择取决于各种因素。为了帮助指导您的决定,我们汇总了一些基本的经验法则:
如果您仍然不确定自己的最佳制造方法,请与我们的工程师联系并上传您的设计。 Chiggo是 CNC加工和中国的3D打印服务的领先提供商,并在这里有一支经验丰富的团队为您提供帮助!
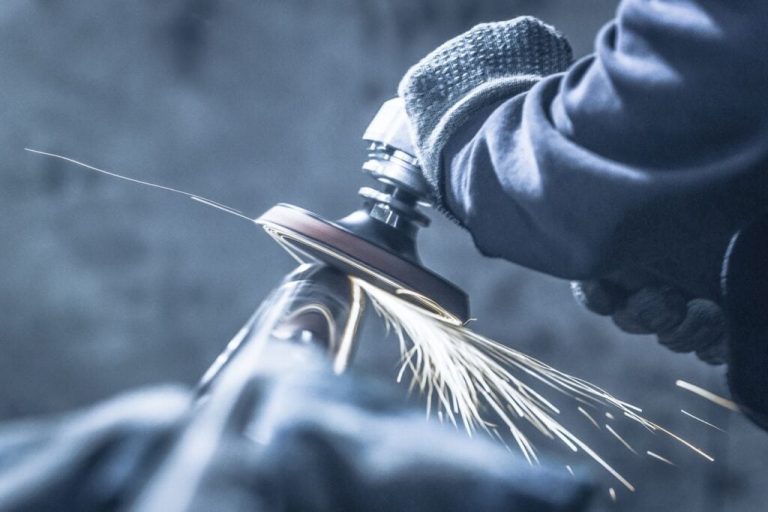

由于暴露于氧气,水分,高温和机械磨损,金属成分往往会随着时间而变化。抛光会产生镜面平滑的表面,可最大程度地减少腐蚀起始位点并防止表面污染。最终的饰面增强了装饰吸引力,并为功能用途(例如光反射器)提供了高反射率。此外,通过消除表面不规则性,抛光消除了充当应力浓缩剂的微型注释,从而改善了疲劳寿命。
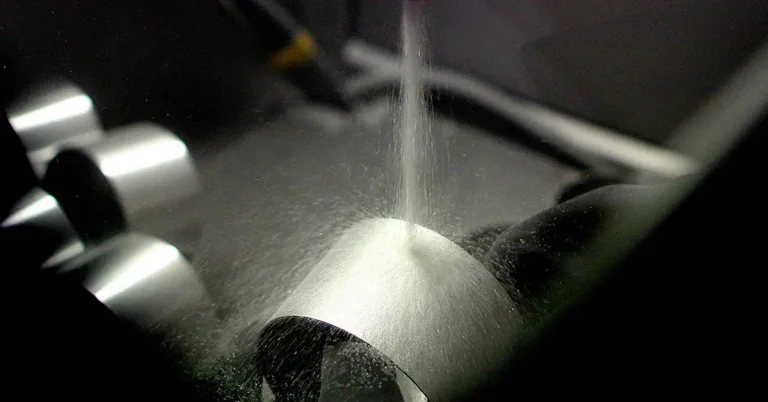

珠子爆破是一个小球磨蚀剂(通常是玻璃或陶瓷珠)的过程,在高压面向表面的过程中被推动。

聚丙烯(PP)和丙烯腈丁二烯苯乙烯(ABS)是现代制造中使用最广泛的两种热塑性塑料。两者都是负担得起的,可回收的,并且可以很好地与CNC加工,注塑成型和工业3D打印。尽管它们相似,但PP和ABS在化学结构,机械性能和环境性能方面有显着差异。

عربي
عربي
中国大陆
简体中文
United Kingdom
English
France
Français
Deutschland
Deutsch
नहीं
नहीं
日本
日本語
Português
Português
España
Español