English

Capacidades
Prototipagem rápida e fabricação sob demanda.

Indústrias
Junte-se a milhares de líderes do setor que impulsionam a inovação de produtos com a Chiggo.
Dispositivos Médicos
Aeroespacial
Produtos de consumo
Equipamentos Industriais
Fornecendo inovações com rapidez e segurança para a área da saúde
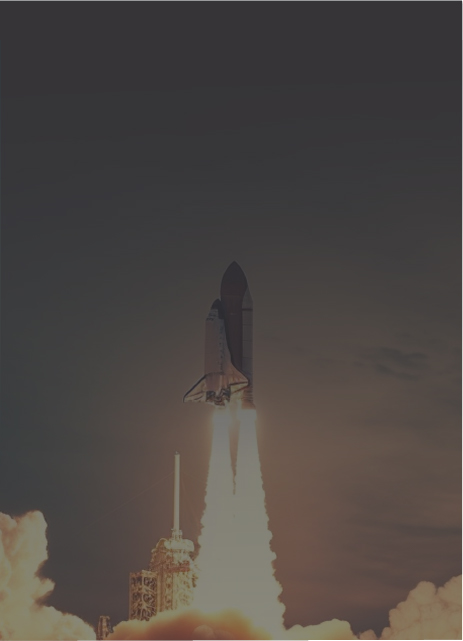
Impulsionando projetos desde o projeto até a decolagem com eficiência
Moldar produtos que definem a vida moderna, da ideia à utilização
Impulsionando o progresso com maquinário avançado para produtividade superior

Soluções
Uma solução completa, desde matérias-primas até produção e aprimoramento de produtos.

Sobre nós
Descubra quem somos e como garantimos qualidade e entrega pontual.
Sobre Chigo
Sobre a entrega
Garantia de qualidade
Nossa fábrica
Nossa visão, missão, histórico de desenvolvimento e equipe dedicada.
Tempos de resposta rápidos e eficientes, otimizando cada etapa, desde a colocação do pedido até a entrega.
Fornecendo prototipagem rápida de qualidade e peças de produção sob demanda que atendem e superam as expectativas.
Descubra a precisão e a inovação por trás da Chiggo com um tour pela nossa fábrica, disponível online ou no local.

Recurso
Tudo o que você precisa saber sobre fabricação digital.
-
Blogue
-
Vídeo
Sua fábrica de fontes confiáveisDesde 2011











-NC加工-448X301.jpg?width=448&height=301)














































